There was a time when everyone had the option to buy software with a one-time payment and install it on a computer without paying any recurring charges. It was a golden era, and everyone loved the idea of paying in full instead of spending in chunks for their entire lives.
However, the new transformation came around a decade ago, when software companies started offering a subscription model. This idea gained popularity due to various reasons, like customers get the option to avail all the premium features of a software for an affordable price point instead of getting a lifetime license.
SaaS, Software as a Service, is a business model that is tried and tested, popular around the globe. Almost every technology giant offers their product with a subscription option. Let’s get started by knowing what the SaaS model is and how it works.
SaaS Business Model: Definition
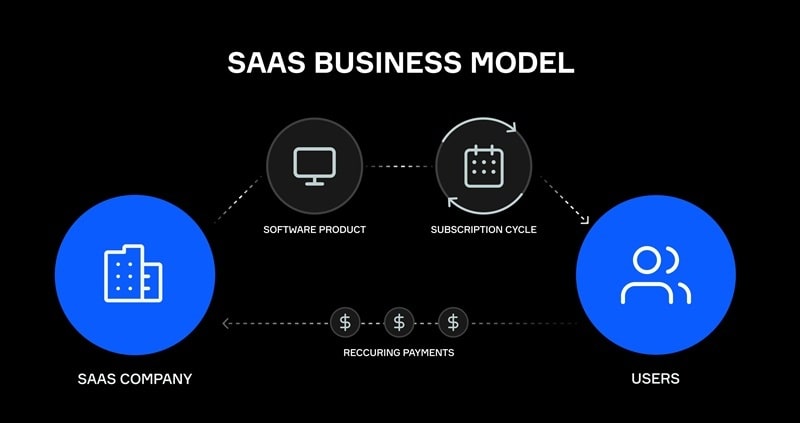
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It is a software delivery model where applications are offered by a publisher to customers over the internet on a subscription basis. In this business strategy, companies offer their software for subscription only, where you can choose to pay monthly, quarterly, or annually. By this, companies have better control over controlling piracy of their product. The software or application a customer uses is fully available on the device, but it connects with the internet to check the status of the subscription before letting the customer use all the features. Due to these reasons, the SaaS business model is widely preferred by almost every technology company.
Examples of SaaS Business Model
Most companies have switched from offering their product for a lifetime license to a subscription model. So, finding a SaaS product in day-to-day life is easier these days. You might be interacting with or using SaaS products daily without even noticing the strategy. Here are some top examples:
1. Slack or Microsoft Teams:
Both Slack and Microsoft Teams are software from the Communication and collaboration category. Slack and Microsoft Teams are used for messaging between teams and to share files in a corporate environment.
2. Canva or Figma:
Canva and Figma are popular choices for designers and creative people, where users get the option to buy a subscription for premium features.
3. Asana or Trello:
If you work in corporate, then you may know about these tools used for task tracking and project workflow. Both companies offer a free plan with limited features, but for corporates, they have many interesting functions available for a subscription price.
4. Salesforce or HubSpot:
Salesforce is a CRM program that is used for customer relationship management. HubSpot is also a CRM with similar functions. To manage a large company, both tools offer functionalities for sales, scalability of business, and much more. With the subscription, you can access a variety of features.
5. Google Meet and Zoom
Both tools are used for video conferencing purposes, where you can find many amazing features like group video call, unlimited group meeting, no time cap, and a lot more with the subscription. Even premium plans offer social media streaming and cloud storage to record the session.
If you look at the software mentioned above, you can find a free-to-use plan. So, all these companies use two different strategies where the publisher uses a freemium business model to attract more users. When the users started getting used to the functionality, the subscription plans became easy to sell. The free model usually comes with limited features and functions, which slowly frustrate users to upgrade when they move to a corporate environment.
Advantages of the SaaS Business Model
The SaaS business model is advantageous to businesses in several ways, and if a well-established company moves to this model, it becomes easier for them to make more revenue. Below are some of the core benefits that make most companies prefer the SaaS business model:
1. Predictable Revenue Stream
One of the biggest advantages for SaaS providers is the steady flow of recurring income. Instead of relying on one-time purchases, businesses can count on monthly or yearly subscription payments. This predictable revenue helps with planning, scaling, and attracting investors.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
SaaS platforms can easily scale to support more users without major infrastructure changes. Companies simply expand their cloud capacity to handle growth. For customers, this means they can upgrade or downgrade plans based on their needs without buying new hardware or licenses.
3. Global Accessibility
Because SaaS runs on the cloud, customers can access it from anywhere with an internet connection. This gives providers a global reach, and users the freedom to work from any device, whether it’s a laptop, tablet, or smartphone.
4. Reduced Piracy Risk
Traditional software often suffers from piracy issues, but SaaS minimizes this problem since the application is hosted online. Customers must log in to use the product, which makes unauthorized copies much harder to create.
5. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
For customers, one of the biggest advantages is that they always use the latest version of the software. Updates, bug fixes, and new features are handled automatically by the provider, saving users time and effort.
Disadvantages of the SaaS Business Model
1. High Initial Investment for Providers
Building a SaaS product requires significant upfront costs. From development and cloud infrastructure to marketing and customer support, companies need to invest heavily before generating stable revenue.
2. Risk of Customer Churn
Since customers pay monthly or yearly, they can cancel anytime if they are not satisfied. This churn risk means SaaS providers must constantly deliver value and maintain strong customer relationships to retain users.
3. Strong Competition in the Market
The SaaS space is highly competitive, with many companies offering similar solutions. This makes it harder to stand out, and often requires providers to spend more on marketing, sales, and product differentiation.
4. Dependence on Internet Connectivity
For customers, using SaaS requires a stable internet connection. In regions with poor connectivity, this can be a major drawback, as the software may be inaccessible or laggy when needed most.
Conclusion
The SaaS business model has changed the way we use and think about software. It benefits both providers, who get recurring revenue and global reach, and customers, who enjoy flexibility, convenience, and lower upfront costs. However, it also brings challenges like ongoing payments, dependence on internet connectivity, and high competition.



